PRODUCT CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
DANBACH ROBOT JIANGXI.INC. Phone:0086-18801818975Tel:0086-0791-88133135
Fax:0086-0791-88221576
E-mail:info@dbhrobot.com
Address:Nanchang High - tech Zone Innovation No. 811
Definition of AGV and AGC
DANBACH ROBOT
The AGV is the abbreviation of Automated Guided Vehicle. It refers to a transport vehicle equipped with automatic guiding devices such as electromagnetic or optical, which can travel along a prescribed guiding path, with safety protection and various transfer functions. The AGV belongs to the category of WMR-Wheeled Mobile Robot.
AGC (Automated Guided Cart), which belongs to the category of AGV, but because of its unique function and use, it is alone. AGC is a simple AGV technology represented by Japan. The technology pursues simplicity and practicality, and strives to restore the investment cost in the shortest time. This type of AGV is fully integrated with simple production applications (single path, fixed process), AGC is only used for handling, and does not emphasize the automatic loading and unloading function of AGV. Due to the development of Japan's basic industries, AGC manufacturers can configure the AGC with functional devices that are almost simple and can't be simple, making the cost of AGC almost to the limit.
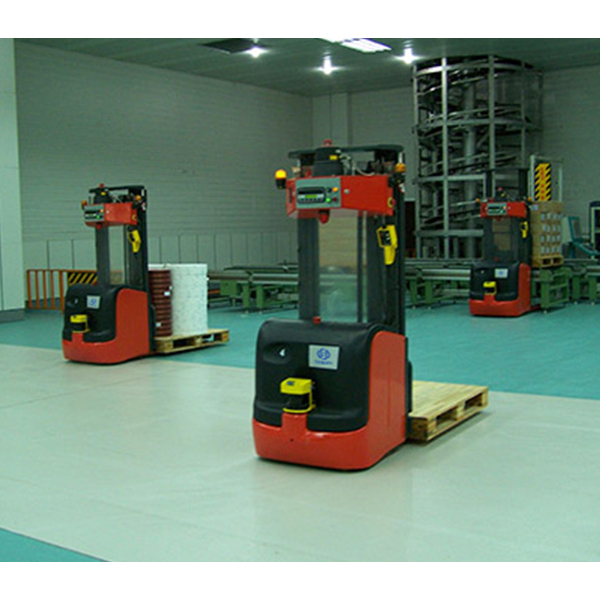

How to choose AGV or AGC?
The control of AGV is relatively complicated, and there are special algorithms from the walking attitude to the scheduling management of multiple vehicles. The AGC is much simpler, and a PLC can do it. Because of the significant differences in functionality and price, users should carefully analyze the requirements to determine AGV or AGC before implementing the project.
Combining the technical characteristics of the two, AGC can be selected when the following conditions are met at the same time.
1. A single path. That is, there is no branch in the loop of the AGV operation, a single loop.
2. A fixed process. That is, the AGV repeats the same action for each task cycle, that is, the position order of each cycle stop point is constant. For example, AGV may need to stop at three points A, B, and C in the cycle. Then A, B, and C are the order of AGV parking. AGV cannot directly go from point A to point C. At point B, whether or not there is work. Have to stop. Of course, the fixed process refers to the preset process, and there can be multiple. But in any case, the process is artificially pre-aware, pre-set, rather than the calculation of the upper computer according to the scheduling strategy.
3. the guidance and positioning accuracy of the AGV is not high, just AGV to transport the goods to the approximate location.
4. No transfer mechanism is required, usually by manual loading, unloading or using drag-and-drop AGC.
In addition, there are multiple branches, multiple loops, complex paths with merged and shunted flows, variable processes, high positioning requirements, and more complicated loading and unloading tasks. , you should choose AGV.
Previous:How to improve the efficiency of AGV warehousing logistics robots?
next:Palletizing robot is one of the important equipment